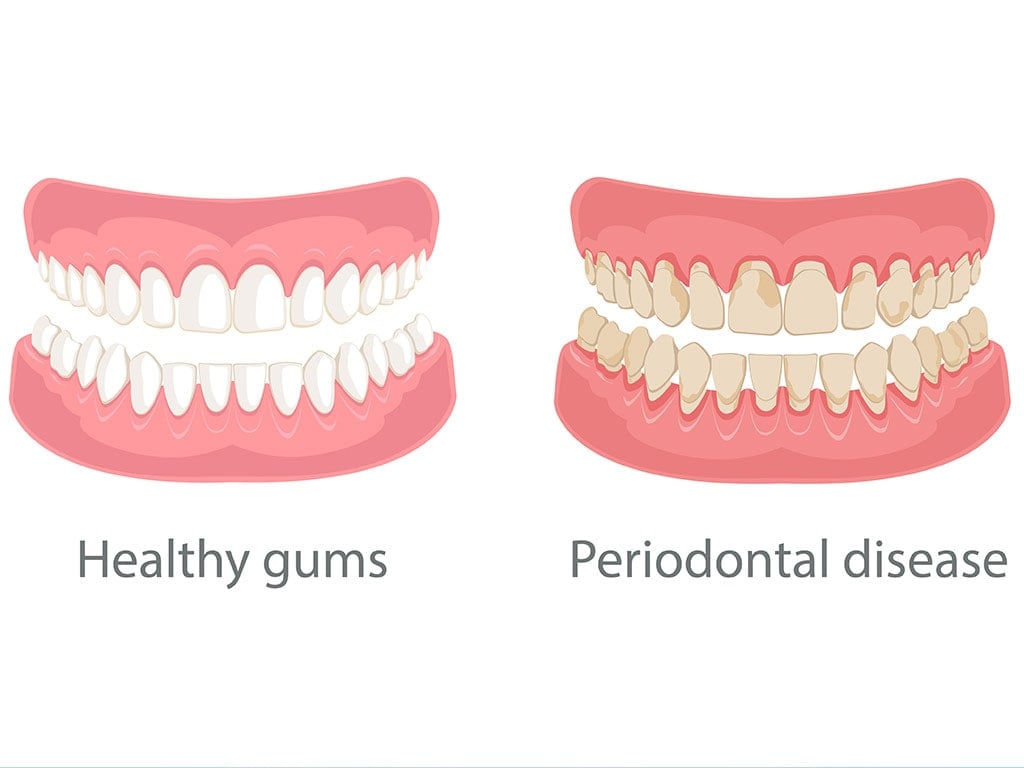
Symptoms of Gum Disease
Gum disease is where gums become infected or start to recede. It is also called periodontitis and can lead to tooth loss. Symptoms include swollen gums, bright red or purple gums, bleeding gums, bad breath, and pus between gums and teeth.
Benefits of Treating Gum Disease
Treating gum disease will make you feel better because you won’t suffer from gum pain or bleeding gums. It also reduces the chances of infection and prevents cavities and tooth loss.
Scaling and Root Planing
One non-surgical way to treat gum disease is with the dentist scaling and root planing the gums. This is done during deep cleaning procedures. Scaling is when the dentist goes below the gumline to remove both plaque and tartar. The gum can then be reattached to teeth.
Root planing is removing infected teeth structures and smoothing out root surfaces.
Pocket Reduction Surgery
Gum disease can result in pockets between the gum and teeth where plaque and bacteria gather. Those that can be corrected with non-surgical procedures must be fixed with pocket reduction surgery.
Surgery reduces the size of the pocket and can save the tooth. The periodontist also removes all the plaque and tartar below the gumline during surgery and may use regenerative methods to encourage new bone to grow.
Guided Tissue Regeneration
Guided Tissue Regeneration (GTR) is the process of stimulating new bone around teeth and deteriorated gums. It helps the roots be stronger and extends the tooth’s life by providing more stability. It uses an artificial membrane that stops soft tissue from growing into gaps and allows the slow-growing bone to grow instead.

Management of Gum Disease
Gum disease, once it starts, will never completely be eliminated but can be managed with deep cleanings, oral hygiene care, and regular dental visits. The best thing to do for gum disease is to prevent it. Your dentist can give you ways you can prevent it from ever occurring.
Antibiotics for Treatment
Your dentist will probably prescribe antibiotics to take before or after each of the gum disease treatments. This is an important part of the protocol to keep gum infections from continuing or spreading.
Six Steps to Gum Disease Treatment
1. Preparation for Deep Cleaning
Your dentist will need to do a thorough evaluation of your medical history and dental history before doing a deep cleaning to resolve gum disease. That will include an X-ray and a surface cleaning by a hygienist as well as a physical examination of your mouth.
2. The Second Appointment
The deep cleaning will be done in a second appointment. The dentist will first give you local anesthesia to prevent you from feeling pain. This is usually a combination of a topical numbing agent followed by an injection.
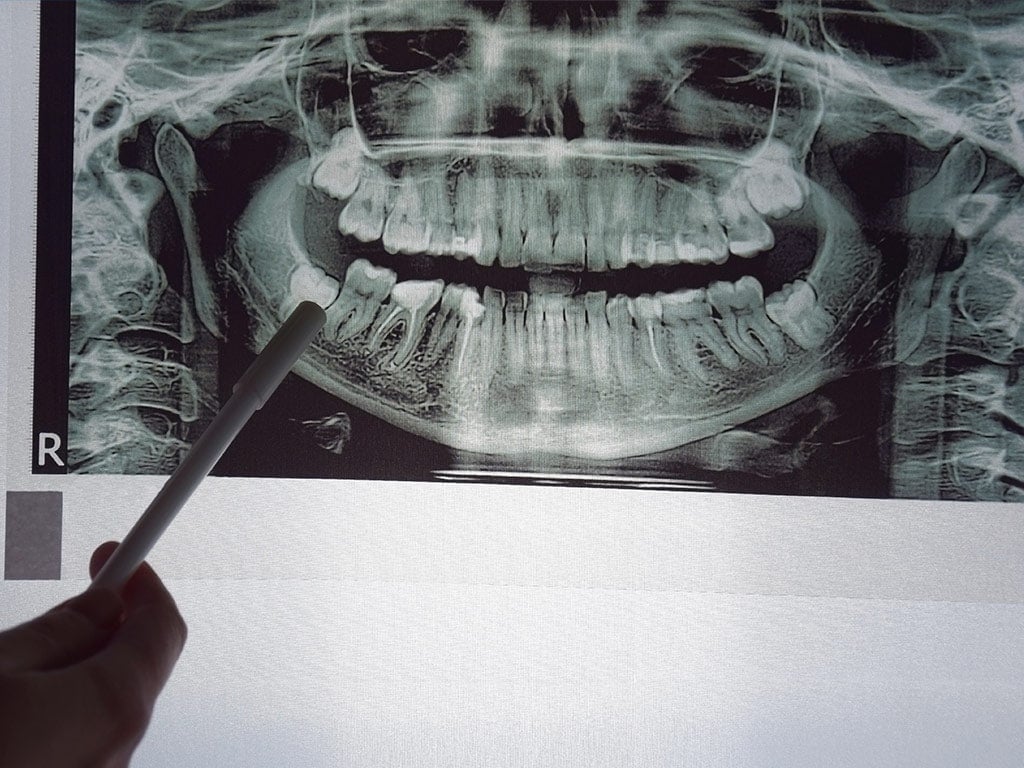
3. Gum Probe
Once the area is numbed, the dentist will probe the gums to determine the extent of the disease and the worst area. They will decide if you have gingivitis or periodontitis. That determination will affect how they handle the rest of the procedure.
4. Scaling Starts
The dentist uses a tool called a scaler to remove plaque. An ultrasonic tool with a water spray may also be used. The difference between this procedure and regular dental cleaning is the dentist will go below the gum line.
5. Planing the Roots
The next step in the procedure is root planing. This is when the dentist smooths rough spots on the teeth’s roots by using a rubbing motion. This prevents bacteria from sticking to the surfaces of the teeth.
6. Adding Fluoride and Flossing
The final stage of the treatment is to finish off with fluoride. The dentist or hygienist will then floss your teeth.
Schedule a Gum Disease Consulation
Frequently Asked Questions About Gum Disease
Can young people get gum disease?
While it’s rare for younger people to get gum disease, it can happen. Those who get gum disease are typically those who have increased plaque and tartar problems. That can come from dry mouth or improper oral care.
Is gum disease linked to other health problems?
There are unexplained links between gum disease to other diseases including Alzheimer’s, asthma, diabetes, heart disease, osteoporosis, kidney disease, and cancer. More than 120 health conditions are linked to dental problems.
What causes gum disease?
Most dentists attribute gum disease to bad brushing and flossing habits. You should brush your teeth twice a day and floss at least once a day.